Pipeline
Camel supports the Pipes and Filters from the EIP patterns in various ways.
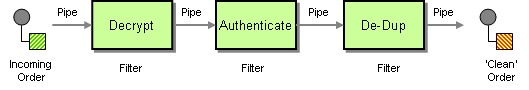
With Camel, you can separate your processing across multiple independent Endpoints which can then be chained together.
Options
The Pipeline eip supports 0 options, which are listed below.
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
note | Sets the note of this node. | String | |
description | Sets the description of this node. | String | |
disabled | Disables this EIP from the route. | false | Boolean |
outputs | Required | List |
Using pipeline
You can create pipelines of logic using multiple Endpoint or Message Translator instances as follows:
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("activemq:cheese")
.pipeline()
.to("bean:foo")
.to("bean:bar")
.to("activemq:wine");<route>
<from uri="activemq:cheese"/>
<pipeline>
<to uri="bean:foo"/>
<to uri="bean:bar"/>
<to uri="activemq:wine"/>
</pipeline>
</route>- route:
from:
uri: activemq
parameters:
destinationName: cheese
steps:
- pipeline:
steps:
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: foo
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: bar
- to:
uri: activemq
parameters:
destinationName: wineThough a pipeline is the default mode of operation when you specify multiple outputs in Camel. Therefore, it’s much more common to see this with Camel:
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("activemq:SomeQueue")
.to("bean:foo")
.to("bean:bar")
.to("activemq:OutputQueue");<route>
<from uri="activemq:cheese"/>
<to uri="bean:foo"/>
<to uri="bean:bar"/>
<to uri="activemq:wine"/>
</route>- route:
from:
uri: activemq
parameters:
destinationName: cheese
steps:
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: foo
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: bar
- to:
uri: activemq
parameters:
destinationName: winePipeline vs Multicast
The opposite to pipeline is multicast. A Multicast EIP routes a copy of the same message into each of its outputs, where these messages are processed independently. Pipeline EIP, however, will route the same message sequentially in the pipeline where the output from the previous step is input to the next. The same principle from the Linux shell with chaining commands together with pipe (|).
When using a pipeline is necessary
Using a pipeline becomes necessary when you need to group together a series of steps into a single logical step. For example, in the example below where Multicast EIP is in use, to process the same message in two different pipelines. The first pipeline calls the something bean, and the second pipeline calls the foo and bar beans and then routes the message to another queue.
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("activemq:SomeQueue")
.multicast()
.pipeline()
.to("bean:something")
.to("log:something")
.end()
.pipeline()
.to("bean:foo")
.to("bean:bar")
.to("activemq:OutputQueue")
.end()
.end() // ends multicast
.to("log:result");Notice how we have to use end() to mark the end of the blocks.
<route>
<from uri="activemq:SomeQueue"/>
<multicast>
<pipeline>
<to uri="bean:something"/>
<to uri="log:Something"/>
</pipeline>
<pipeline>
<to uri="bean:foo"/>
<to uri="bean:bar"/>
<to uri="activemq:OutputQueue"/>
</pipeline>
</multicast>
<to uri="log:result"/>
</route>- route:
from:
uri: activemq
parameters:
destinationName: SomeQueue
steps:
- multicast:
steps:
- pipeline:
steps:
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: something
- to:
uri: log
parameters:
loggerName: Something
- pipeline:
steps:
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: foo
- to:
uri: bean
parameters:
beanName: bar
- to:
uri: activemq
parameters:
destinationName: OutputQueue
- to:
uri: log
parameters:
loggerName: result